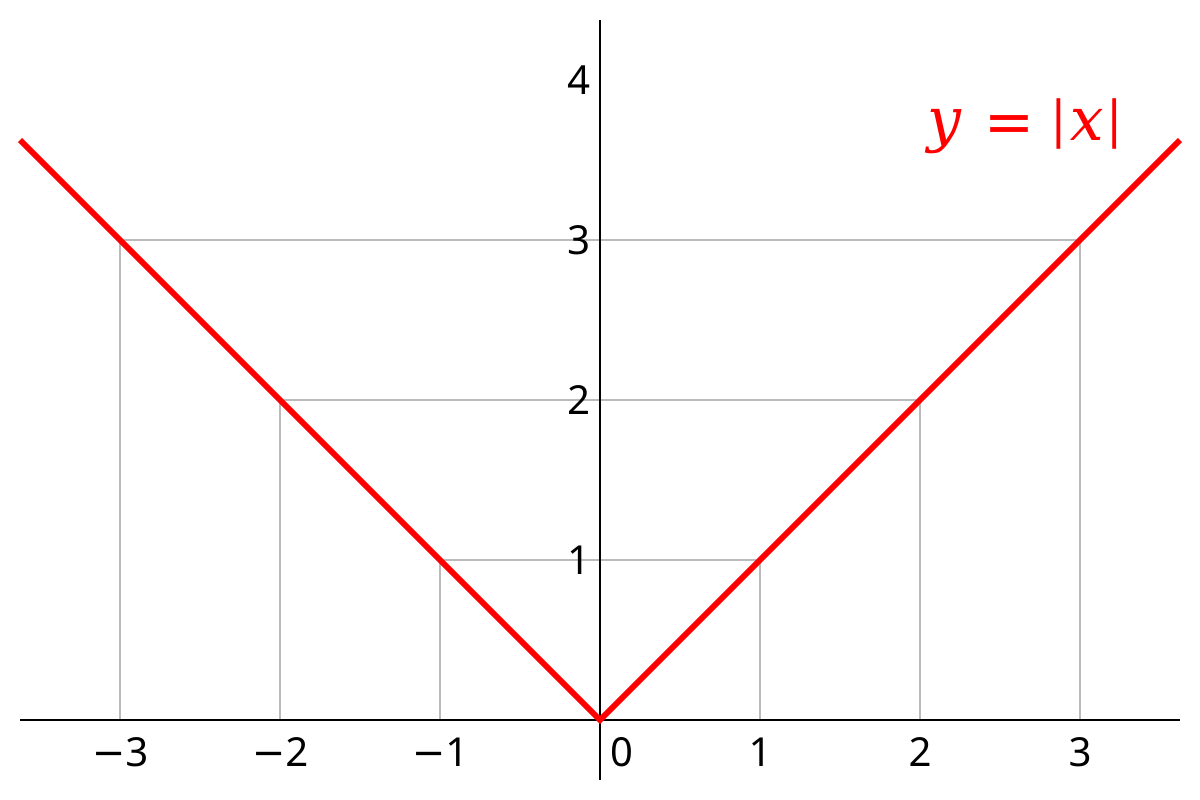
 For example, the absolute value of 3 is 3, and the absolute value of −3 is also 3. The absolute value of a number may be thought of as its distance from zero. Generalisations of the absolute value for real numbers occur in a wide variety of mathematical settings.
For example, the absolute value of 3 is 3, and the absolute value of −3 is also 3. The absolute value of a number may be thought of as its distance from zero. Generalisations of the absolute value for real numbers occur in a wide variety of mathematical settings.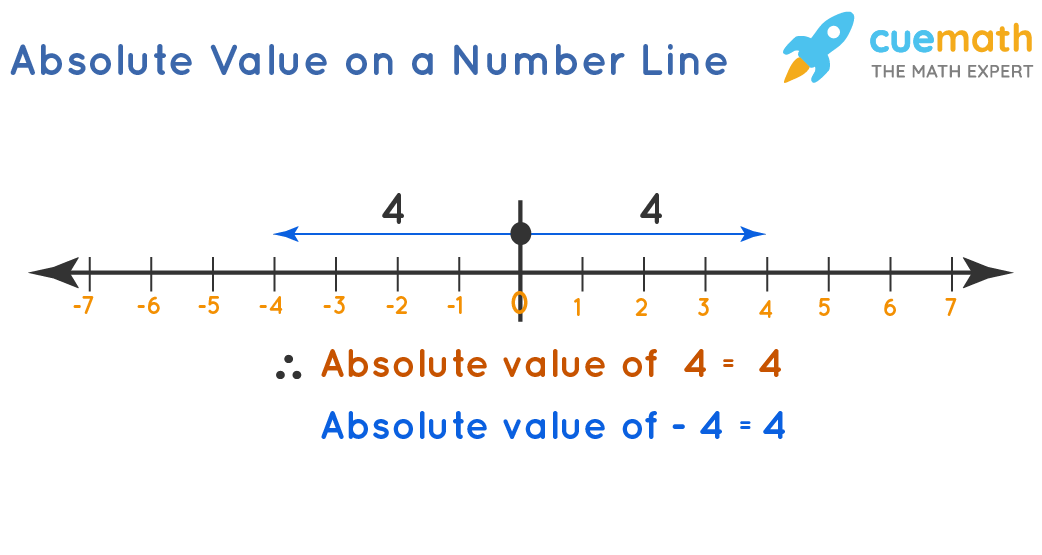 The absolute value of a number is defined as its magnitude irrespective of the sign of the number. To find the absolute value of a real number, we consider only the number and remove the sign.
The absolute value of a number is defined as its magnitude irrespective of the sign of the number. To find the absolute value of a real number, we consider only the number and remove the sign.