 Human ear, organ of hearing and equilibrium that detects and analyzes sound by transduction and maintains the sense of balance. Anatomically, the ear has three distinguishable parts: the outer, middle, and inner ear.
Human ear, organ of hearing and equilibrium that detects and analyzes sound by transduction and maintains the sense of balance. Anatomically, the ear has three distinguishable parts: the outer, middle, and inner ear.:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/article/en/the-ear/ITkF2vN4DoW1bfNzI6ZrQ_WhaN0cJk5bhxsOyTbubRNA_Auricula_02.png) The ear is the sensory organ for hearing and balance and it is anatomically divided into 3 parts: the external, middle and internal ear.
The ear is the sensory organ for hearing and balance and it is anatomically divided into 3 parts: the external, middle and internal ear.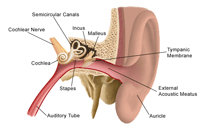 Hearing starts with the outer ear. When a sound is made outside the outer ear, the sound waves, or vibrations, travel down the external auditory canal and strike the eardrum (tympanic membrane).
Hearing starts with the outer ear. When a sound is made outside the outer ear, the sound waves, or vibrations, travel down the external auditory canal and strike the eardrum (tympanic membrane).